field permeability testing|how to calculate soil permeability : makers Field permeability tests gave the local hydraulic conductivities (K) at three different sites. Constant head (CH) and variable head (VH) tests were performed using 33 monitoring wells (MWs) installed in confined aquifers. Each test method was conducted with either an inward flow from aquifer to pipe or outward flow from pipe to aquifer, which .
webVocê não conseguirá encontrar esses vídeos de sexo barbiethreesix em nenhum outro lugar, barbiethreesix é uma das muitas modelos de tendências no momento e você .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web24 de jun. de 2022 · Siga o PORTAL DO ZACARIAS no Facebook, Twitter e no Instagram. Entre no nosso Grupo de WhatApp e Telegram . Ou as razões por trás de suas ações perversas. A única coisa certa aqui era sua completa serenidade depois de terem cometido esses atos abomináveis. Fonte: Mega Bizarro.
WATER TESTING FOR PERMEABILITY. General. Most rock and soil contains numerous open spaces where water may be stored and through which water can move. Permeability, or hydraulic conductivity, is a measure of the ease of movement of fluid and gas through the open spaces .
The method involves the insertion of a tube into the soil to the depth where the measurement is desired, the removal of the soil from the tube, the emptying of the water in the tube to a known .
1.1 This test method covers field measurement of hydraulic conductivity (also referred to as coefficient of permeability) of porous materials using a cased borehole technique.When isotropic conditions can be assumed and a flush borehole is employed, the method yields the hydraulic conductivity of the porous material.For this article, we will examine various field tests of soil and the equipment required to perform them. Soil Penetration Tests. The pocket-type penetrometers and shear testers discussed in Soil Classification: . Field measurements of .The test measures the permeability (k) of the soil and because it is carried out in-situ provides a more reliable result than can be determined in the laboratory. Implementation of the test and interpretation of the results requires . Field permeability tests gave the local hydraulic conductivities (K) at three different sites. Constant head (CH) and variable head (VH) tests were performed using 33 monitoring wells (MWs) installed in confined aquifers. Each test method was conducted with either an inward flow from aquifer to pipe or outward flow from pipe to aquifer, which .
soil permeability testing pdf
FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is defined
Abstract. Pressure transducers (PTs) and an atmospheric pressure transducer (APT) were used to register test data during two types of permeability tests, which were performed in 14 wells monitoring a confined aquifer installed in the lab, and a field rising-head test in clay. The constant-head tests were performed using a peristaltic pump and thus .These tests are carried out in the field on the soil/rock in situ around the borehole. They therefore avoid the problems of obtaining representative undisturbed samples that limit the usefulness of laboratory testing. . it may be possible to carry out a series of permeability tests after the end of drilling by isolating sections of the .
The field permeability tests are carried out to determine permeability of each subsurface strata encountered up to bed rock as well as to ascertain overall permeability of strata. The tests are carried out in standard drill holes where subsurface explorations for foundations are carried out by drilling. The tests are also carried out in auger Magnetic field testing measures the degree by which the presence of a magnetic field will effect a material. This property of being attracted to a magnetic field is known as paramagnetism. If your products are being used in an environment, such as those around an MRI, it will be important for your customer to know if your product is paramagnetic.
soil permeability chart
A simple field test for estimating soil permeability; A more precise field test measuring permeability rates. The visual evaluation of the permeability rate of soil horizons. The permeability of individual soil horizons may be evaluated by the visual study of particular soil characteristics which have been shown by soil scientists to be closely .
1. The USBR 730089, “Procedure f- or Performing Field Permeability Testing by the Well Permeameter Method” (Section 2.4). Note: the result must be converted to an infiltration rate. 2. The Percolation Test per RCDEH (Section 2.3) may be used. Note: the result must be converted to an infiltration rate. Laboratory Tests vs. Field Tests. Soil permeability tests fall into two main categories: laboratory and field tests. Laboratory tests, such as the constant head and variable head permeameter tests, are controlled and precise. They’re ideal for granular soils like sand, where water moves freely. In a different way, field tests are designed to . 4. Testing Procedure for Permeability in a Triaxial cell using Clisp Studio. This test refers to the Constant head permeability method. At the time of writing, VJ Tech complies to BS1377-6:1990, EN ISO 17892-11 and D5484-16 (Method A).. a.Field Permeability Testing of Pavement; Calculating the Coefficient of Permeability; Asphalt permeability has a direct impact on the performance and longevity of pavements. Long-term internal exposure to water and water vapor in the asphalt voids is a significant factor in the premature deterioration of roadways. Air and water promote oxidation .
how to calculate soil permeability
Field studies at the Dead Sea, Israel, and in Oslo have indicated that serious errors may be introduced in estimating the permeability of fine-grained clay soils using in situ tests if excessive water pressures are used, a fact already appreciated by rock and petroleum engineers. Model laboratory tests in London have confirmed that very low pressures must be employed and a .A FIELD METHOD FOR MEASURING THE PERMEABILITY OF SOIL BELOW A WATER TABLE' RICHARD K. FREVERT, Research Associate Professor of Agricultural Engineering AND DON KIRKHAM, Research Associate Professor of Soils and Associate Professor of Physics, Iowa State College SYNOPSIS The measurement of water permeability of soil under field .
Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant and falling head laboratory tests on intact or reconstituted specimens. Alternatively, permeability may be measured in the field using insitu borehole permeability testing (e.g. [2]), and field pumping tests.IS 5529-2 (2006): In-situ Permeability Tests, Part 2: Tests in Bedrock [WRD 5: Gelogical Investigation and Subsurface Exploration] / . and practices prevailing in different countries in addition to relating it to the practices in this field in the country. This standard was first published in 1973 and revised in 1985. This revision has been .
This video shows how to perform a falling head permeability test for fine-grained soil. This test is typically performed on fine-grained soil with low permea.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or when used as base courses under pavements.The permeability of a soil is reported in metres per second (m/s), usually in engineering notation due to the small magnitude of the number e.g.: 1E-9 m/s. What is a permeability test? Laboratory Permeability testing can be undertaken using 3 different procedures in accordance with Australian Standards AS1289.Permeability variability was computed from test data derived from field cores and specimens prepared in the laboratory. Repeat tests by different operators indicated differences that warrant additional investigation.Flexible wall permeability testing determines hydraulic conductivity or flow characteristics of water or other permeants through soils and is commonly used to assess natural soils, fills, or clay liners in environmental and geotechnical applications. . Double-Ring Infiltrometer is a field device for measuring the infiltration of water or .

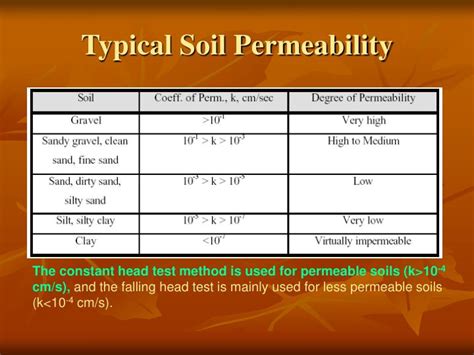
Field experience is examined and capable field permeability test methods are identified. Specifications for test borehole preparation, test performance, and methods of analysis are given. The test methods are comparatively rated in a matrix with respect to costs, ease of use, and data effectiveness for a broad range of conditions.NOTE 2 For most types of ground, field permeability tests yield more reliable data than those carried out in the laboratory, because a larger (although still modest) volume of material is tested, and because the ground is tested in situ, thereby avoiding the disturbance associated with sampling. . Permeability tests should be carried out by . The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 – Part 36, 1975). Furthermore, the field coefficient of permeability was measured using pumping tests at the same site. The measured permeability values are compared to the values empirically deduced from the cone .
field permeability test procedure
field permeability test in borehole
difference between permeability and seepage
Endereço. Rua Lord Crockane, 625 – Ipiranga – São Paulo SP. Horários de funcionamento: Quarta: 17h00 às 00h00. Quinta e Sexta: 17h00 às 01h00. Sábado: 12h00 às 01h00. .
field permeability testing|how to calculate soil permeability